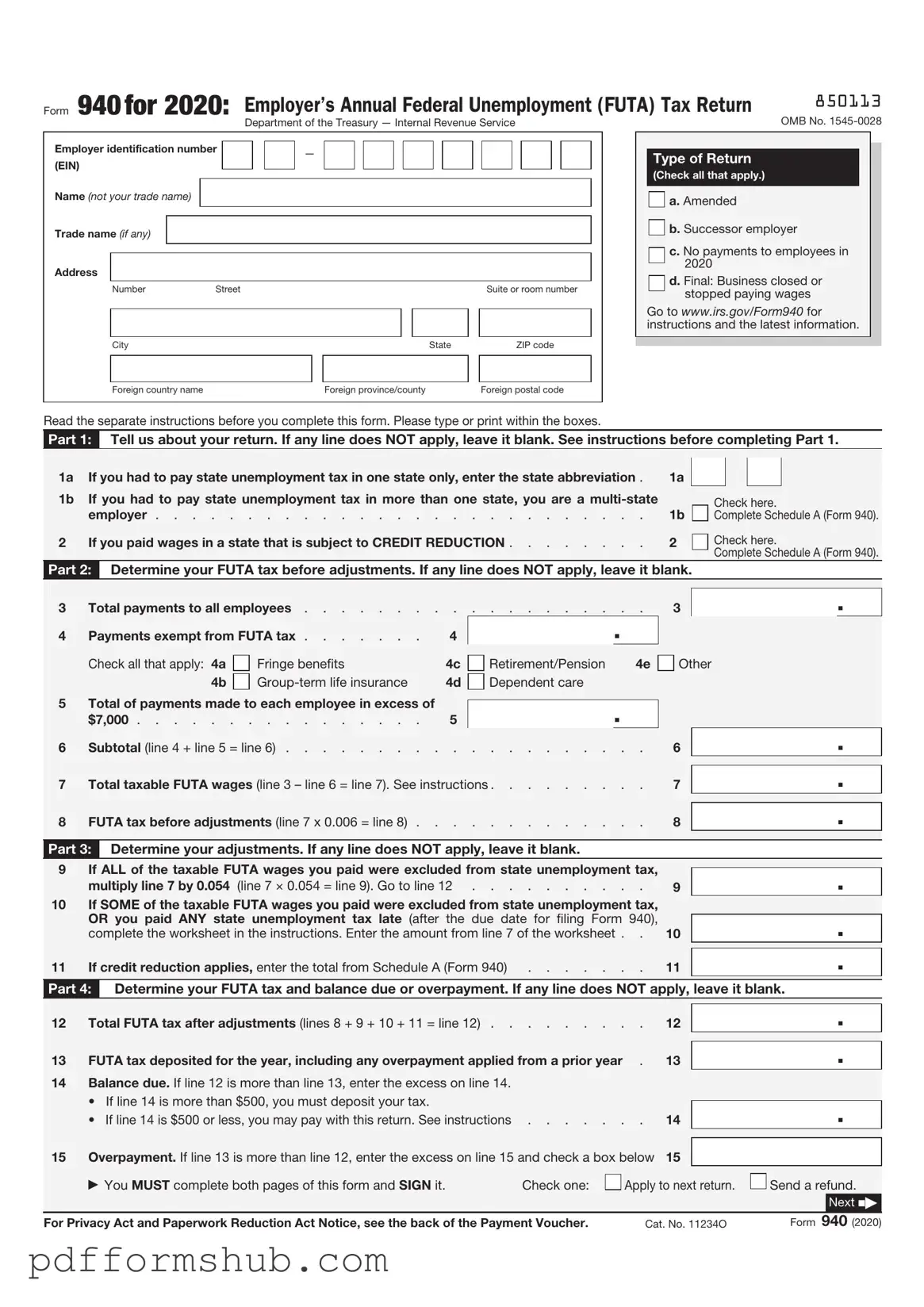
Fill in Your IRS 940 Form
The IRS 940 form is an annual tax return used by employers to report their Federal Unemployment Tax Act (FUTA) liabilities. This form helps the IRS track unemployment taxes owed by businesses, ensuring compliance with federal regulations. Understanding its requirements is crucial for employers to avoid penalties and maintain proper records.
Ready to fill out the IRS 940 form? Click the button below to get started!
Customize Form
Fill in Your IRS 940 Form
Customize Form

Customize Form
or
Free PDF Form
Short deadline? Complete this form now
Complete IRS 940 online without printing hassles.